SPF stands for Sender Policy Framework and is a protocol that determines whether the sender of an email is authorized to send messages from a specific mail server. The main purpose of SPF records is to prevent spam, but more importantly for you:
The SPF record informs other internet services that your email truly originates from your website, preventing your emails from being filtered into the spam folder!
Where can you add the SPF record?
You need to add the SPF record at your web host. When registering your domain name, you should have received login credentials from your web host that allow you to modify the DNS settings of your domain name.
The structure of an SPF record
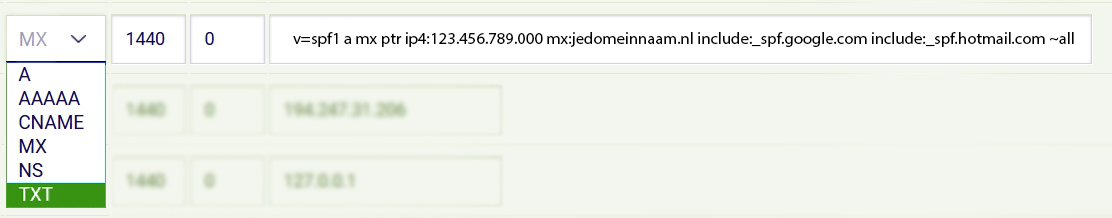
First, you need to indicate that the record is an SPF record by adding the following:
v=spf1
This tells the DNS which version of SPF you are using, which is important for reading the SPF record.
Next, you specify when an SPF is valid:
all for all outgoing mail servers.
a If the sender’s IP address matches the IP address (A record) of the domain.
mx When the mx record matches the SPF address.
ip4 & ip6 When the mail is sent, it is transmitted via IP addresses (of your domain).
Okay, there are many possibilities, what is common?
v=spf1 a mx ptr ip4:123.456.789.000 mx:yourdomain.com include:_spf.google.com include:_spf.hotmail.com ~all
Note: Choose TXT as the record type and replace the crossed-out information with the IP address of your own server/website and your own domain name.